Catch Weight Management in SAP for the Food Industry
SAP Business OneCatch weight: What it is, why it matters, and how to use catch weight management in SAP Business...

February 18, 2020
Blog > Expiry Date Management: What Does SAP Life Sciences Mean for Manufacturers?
Life is short. So too is the life of products in the life sciences industry. For food and beverage manufacturers, expiry data is based on the defined shelf life of the product established from its production date. In the life sciences industry, however, the life of biomedical tissue, blood products, etc. is based on the batch with the shortest expiry date. Here’s how life sciences companies can manage variations in expiry date calculation in the SAP Life Sciences solution to streamline conducting business with their supply chain partners.
But first, what are some supply chain challenges with shelf-life expiry dates?
When dealing with life sciences products, manufacturers face visibility challenges with supply chain partners. Because some products require a minimum shelf life before they can enter a supply chain, it’s critical to know how to calculate shelf life in an industry where perishability is a concern. Products in a warehouse must first possess the required remaining shelf-life data before moving to production. When working with a complex supply chain, it comes down to having a system that both records expiry dates and shares the data throughout a business as components are used to manufacture finished products. As a life sciences business grows, quality control and a consistent process that simplifies expiry date calculation increase in importance.
To manage variations in expiry date calculation, the SAP Life Sciences solution, SAP Business One, offers several options. The screenshot below demonstrates how you can select the Expiry Evaluation temaplate to use in the Item Details screen.
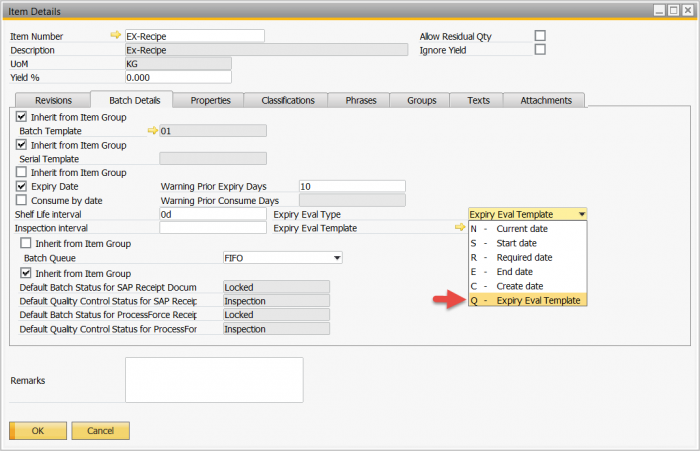
The most complex expiry date calculation is the ‘expiry date inheritance’ method. This expiry date calculation, which you can see in the following screenshot, enables businesses to determine their rules and methods for managing their inheritance data.
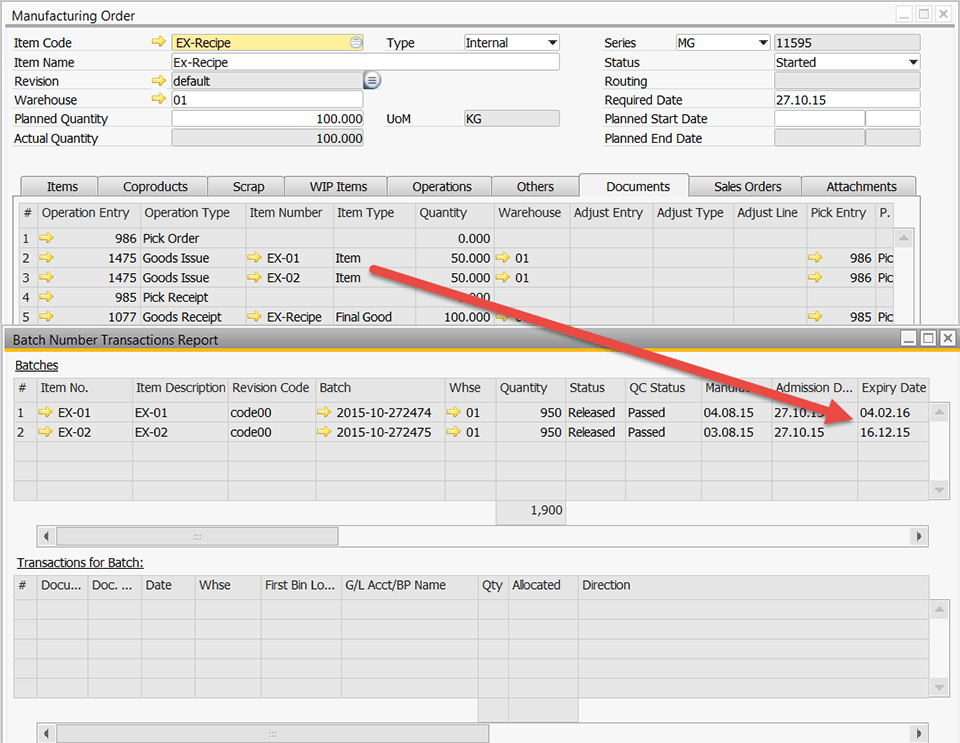
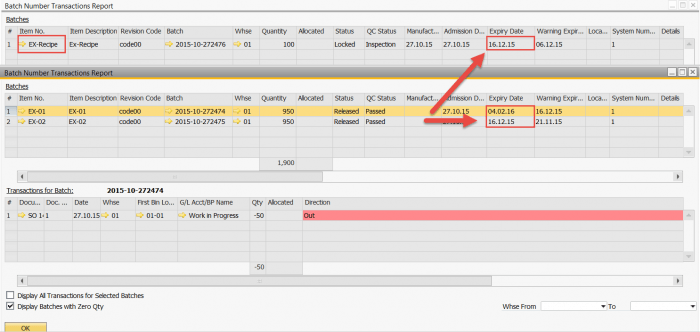
During the production process, the manufacturing order consumes two batches of materials, each with a different expiry date, as displayed by the Batch Transaction Report below, where item EX-02 has the youngest expiry date of 12.16.15.
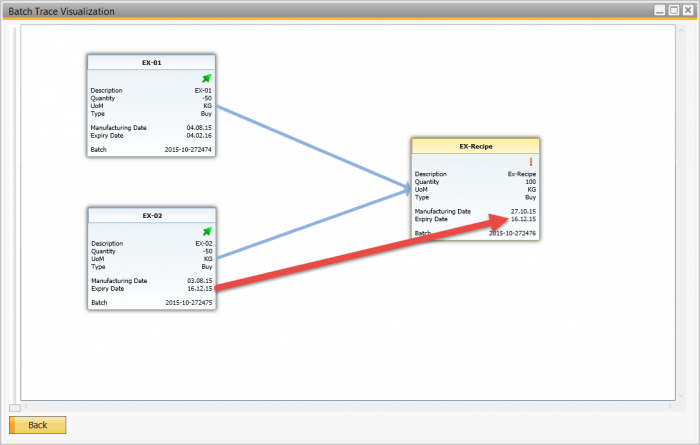
The Batch Trace Visualization diagram helps overcome the challenge of traceability, by displaying the traceability of the material batches used in the finished product. This displays the finished product batch expiry date with the same date as the youngest expiry date of the consumed batch, while the Batch Transaction Report can provides additional details.
Life is too short to have questions about the SAP Life Sciences solution. Luckily, we have answers in our free brochure, Why Life Sciences Companies Need ERP. Learn about the daily challenges businesses face in the industry, such as expiry date calculation, and top reasons they need ERP solutions like SAP Business One to help them run their operations.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive our latest blog posts, case studies and ERP news delivered straight to your inbox.
Catch weight: What it is, why it matters, and how to use catch weight management in SAP Business...
As the whiskey industry grows, distillers need more advanced cask management, and Brutos is the...
Explore the four SAP Business One Bill of Material (BOM) types—Production, Sales, Assembly, and...
Recieve our latest blog posts, case studies, and ERP news
delivered straight to your inbox.